WHO SMART Trust
1.1.3 - v1.1.3
WHO SMART Trust
1.1.3 - v1.1.3
This page is part of the Trust (v1.1.3: Release) based on FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) R4. The current version which supersedes this version is 1.4.0. For a full list of available versions, see the Directory of published versions
This digital health trust network is a network of stakeholders that securely exchange and uses health information based on trust, security, and privacy principles, and is designed to ensure that health information is handled in a secure, private, and compliant manner. Through the GDHCN, WHO serves as the custodian of a digital health trust network.
In addition to the key concepts used throughout this document, which are defined below, additional documentation may be found on:
The GDHCN Administrative and Operational Framework should be considered the authoritative source of definitions and concepts in case of any discrepancies.
The GDHCN Trust Network is a Trust Network comprised of the GDHCN Secretariat and GDHCN Participants. The GDHCN Trust Network operationalizes Trust Domains through a Trust Network Gateway by enabling bilateral verification and utilization of Verifiable Digital Health Certificates and the utilization of Trusted Services by GDHCN Participants.
The WHO Secretariat serves as the operational and management leadership of the GDHCN, and in this role, the GDHCN Secretariat.
A GDHCN Participant is participant of the Trust Network that adheres to the Terms of Participation and manages the necessary technical infrastructure and governance processes. GDHCN Participants are responsible for making bilateral determinations related to the utilization of Trusted Services.
An Eligible GDHCN Participant is one of the following:
Participation in the GDHCN is subject to the Onboarding Process set forth by the GDHCN Secretariat in its sole and absolute discretion, and in accordance with WHO rules, regulations, policies and practices, as may be amended from time to time. The requirements for the GDHCN Terms of Participation are comprised of the following components:
The individual identified by a GDHCN Participant as having the primary business and programmatic responsibility for the GDHCN Participant for the implementation of the use cases covered by a Trust Domain.
The individual identified by a GDHCN Participant as having the primary responsibility for the management of the Public Key Infrastructure, including the generation of any needed public-private key pairs, and the configuration and management of the connections between the GDHCN Participant’s Public Key Infrastructure and the GDHCN Trust Network Gateway.
The individual designated by a GDHCN Participant as having the primary responsibility for reviewing the requirements related to a Trust Domain on behalf of this GDHCN Participant. This person should be someone that the GDHCN Secretariat can consult in relation to any legal or policy issues that may arise, such as changes to this document or changes to one of its Annexes that defines a Trust Domain.
The individual designated by a GDHCN Participant as having the primary overall responsibility for the security, technical matters and systems infrastructure of this GDHCN Participant for the applicable Trust Domain including ensuring compliance with technical specifications.
A formal application sent via a verifiable and secure channel from an Eligible GDHCN Participant to the GDHCN Secretariat to join the GDHCN Trust Network and participate within a particular Trust Domain.
The processes required for an Eligible GDHCN Participant to join the GDHCN Trust Network. At the successful conclusion of the Onboarding Process, the Eligible GDHCN Participant shall be considered a GDHCN Participant. Sometimes simply referred to as “Onboarding”.
An organization or organizational unit that is responsible for establishing and/or implementing procedures for accreditation of health professions education institutions. See https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1473223/retrieve and https://applications.emro.who.int/docs/em_rc50_r9_en.pdf?ua=1
An organization or organizational unit that is responsible for establishing and/or implementing procedures for licensure, and the licensing of organizations or individuals to provide clinical, health system or public health services within their jurisdiction. Licensing comprises processes through which duly authorized governmental authorities, such as recognized professional organizations, grant permission to an individual or healthcare organization to operate or engage in a medical occupation or profession. See: https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1473223/retrieve and https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/documents/health-systems-strengthening-glossary.pdf.
An organization, or organizational unit, that is responsible for establishing procedures for and/or implementation of activities related to the protection, promotion, and improvement of public health within a specific jurisdiction or domain. May also be referred to as a Ministry of Health, Department of Health, or Public Health Authority.
An organization, or organizational unit, that is responsible for establishing procedures for and/or implementing required activities, both proactive and reactive, for minimizing the danger and impact of acute public health events that endanger people’s health across geographical regions and international boundaries. See: https://www.who.int/health-topics/health-security.
The Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is the trust model based on public key certificates and certificate authorities. It is the means for publishing and distributing Trust Lists comprising the public keys that can be used to digitally verify the issuer of a Verifiable Digital Health Certificates.
Each GDHCN Participant maintains one or more Signing Certificate Authority (SCA), certificates of which are relatively long lived. The SCA issues public key certificates for the national, short lived, Document Signers. The SCA acts as a trust anchor such that relying GDHCN Participants can use the SCA certificate to validate the authenticity and integrity of the regularly changing DSC certificates.
Document Signers utilize the private key of a private-public key pair to digitally sign Verifiable Digital Health Certificates. A single private key is expected to sign a large quantity of Verifiable Digital Health Certificates. The corresponding public key is referred to as a Document Signer Certificate (DSC).
Document Signer Certificates are the public key certificates associated to Document Signers which are issued or recognized by the GDHCN Participant.
The process and technical specifications regarding the management and use of encryption keys for Verifiable Digital Health Certificates, Public Key Infrastructure, and for securing connections with Trusted Services and the Trust Network Gateway.
A Trust Domain consists of:
Universal verifier applications that support different credential standards are complicated by wide variability in format of the credential payloads, signatures, key formats, and key distribution methods. Public keys formats include x509 certificates, JSON Web Key Sets (JWKS), and DID documents. Signing key distribution methods include API gateways, hosted by issuer at a pre-defined URL, embedded in certificates, and by block-chain based resolution. Establishing root of trust by trust anchor or distributing trust list has been accomplished by API gateway, hosted URL, private dissemination and other bilateral sharing agreements.
While some variability is expected in an approach that preserves sovereignty, there are opportunities for alignment in key format and distribution for the sake of fostering interoperability. With that goal, we provide a unifying trust list format to assemble and share public key infrastructure for all credential specifications used by existing trust networks. Importantly, this format does not enforce a particular policy framework for participants of the trust network.
The GDHCN currently supports two means for key distribution of keys using trust lists
A Trust Network is a means to authenticate the encryption public keys used by participants within a network to perform encryption services, verify digital signatures, establish secure connections between systems, and otherwise make use of encryption public keys.
Trust Network
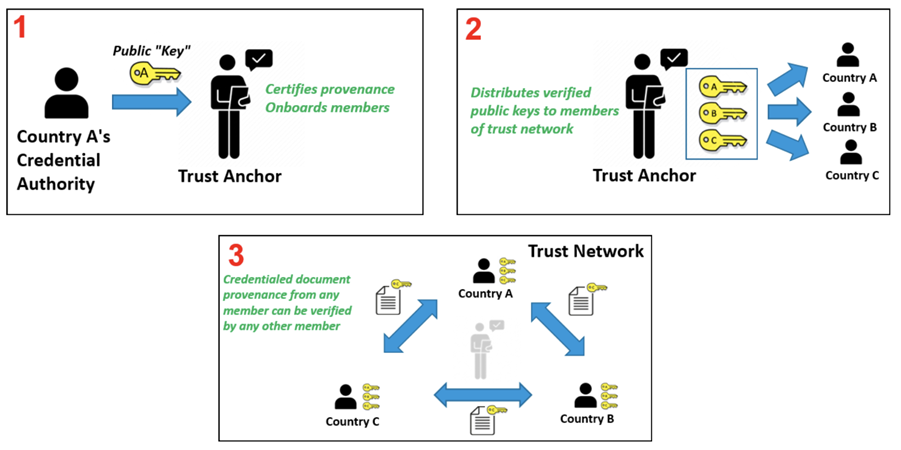
The Trust Network Gateway (TNG) is the open-source software and its IT operational infrastructure, utilizing open standards, for a Public Key Infrastructure and metadata management services which is used to operationalize one or more Trust Domains. The Trust Network Gateway can be interacted with using the API once a mTLS connection has been established.
The Trust Anchor public key certificate of the TNG. The corresponding private key is used to sign the list of all SCA certificates offline.
The TLS server public key certificate of the TNG.
Trust Network Participant (TNP) is an acronym used to label certificates, infrastructure, or technical artifacts made available by GDHCN Participants under the GDHCN Trust Network.
A GDHCN Participant’s Backend System for managing the local part of information. The implementation of GDHCN Participant’s Backend System is not in the scope of this document. A national backend can be also understood as a trusted party on-boarded in the Trust Network Gateway (can be a script, a proxy or a web server as well).
The SCA public key certificate of a GDHCN Participants (could be more than one).
The TLS client authentication public key certificate of a GDHCN Participant’s Backend System.
The public key certificate that a GDHCN Participant uses to sign data packages that are uploaded to the TNG.
A system utilized by a GDHCN Participant to verify the digital signature of a Verifiable Digital Health Certificate.
A service (digital or otherwise) related to the issuance, management, verification, exchange, or other relevant processes, of Verifiable Digital Health Certificates which is defined using open, interoperable digital health standards.
Verifiable Digital Health Certificate: A digital representation of a data set comprising a certificate or document, designed for a set of specific clinical or public health use cases which is defined using open, interoperable digital health standards; that contains within, or is associated to, a digital signature which can be verified by the public key of a public-private encryption key pair, and which is issued by a GDHCN Participant.
The specific Verifiable Digital Health Certificates are defined in the Content Profiles